A dental fistula is a natural bodily reaction to inflammation at the root or tip of a tooth, which can be extremely painful . Here you will find detailed answers to all questions about dental fistula:
apparition
causes
symptoms
treatment
prevention
A tooth fistula does not heal on its own , but must be treated by the dentist in order to avoid serious consequences such as the loss of a tooth or inflammation of the jawbone.
HOW IS AN ORAL FISTULA STRUCTURED?
The word fistula comes from Latin and means tube. The term thus describes a special feature of the fistula: the tube-like duct creates the connection between a collection of pus and the oral mucosa (e.g. the gums).
Dental fistula consists of three parts:
The reason for the fistula is the place of origin, i.e. the abscess directly at the root of the tooth.
The fistula duct or fistula duct forms so that the purulent secretion that has accumulated at the focus of inflammation can be drained to the fistula opening.
The fistula opening is on the gum surface. A painful blister forms here, which is filled with pus.
The development of the fistula in the oral cavity extends over a longer period of time, it can last weeks or even months.
A PATHOLOGICAL FISTULA OFTEN DEVELOPS ON A SINGLE TOOTH
In contrast to abscesses and aphthae , which can form anywhere in the mouth – eg on the palate and tongue – a fistula develops on the gums above the tooth . Usually only a single tooth in the upper or lower jaw is affected.
While mouth ulcers are usually harmless damage to the oral mucosa that can occur as a result of injury, illness or stress and usually heal by themselves, fistulas and abscesses on the tooth are caused by bacterial inflammation . However, an abscess , which can develop as a result of a cyst on the gums, among other things, is larger than a tooth fistula and through theEncapsulation of the pus marked. This pus capsule must be surgically opened, while the accumulated purulent secretion can drain through the fistula duct in the case of a fistula.
A dental fistula can also occur in a child’s mouth
A dental fistula can also occur in a child’s mouth
GERMS ARE AMONG THE PRIMARY TRIGGERS OF TOOTH FISTULA FORMATION
Dental fistula is an inflammatory reaction triggered by a bacterial infestation :
The most common cause is bacterial inflammation of the tip of the tooth root . If the tooth is already damaged, for example by tooth decay , bacteria can get to the root of the tooth and cause an infection.
Inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) is also a potential trigger . Bacteria can easily accumulate in the gum pockets that develop.
A fistula can also develop as a result of inflammation of the periodontium (periodontitis) .
Typical risk factors for the penetration of pathogenic bacteria in the oral cavity are
poor or incorrect oral hygiene
Pressure points from poorly fitting dentures
Oral injuries
a weakened immune system as a result of certain underlying diseases or frequent infections
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
an unhealthy diet with high sugar foods and drinks
FISTULAS IN THE ORAL CAVITY OFTEN REMAIN UNDETECTED AT THE BEGINNING
In the early stages, a tooth fistula usually does not cause any pain. As the inflammation progresses, there is a feeling of pressure or tension on the affected tooth as well as dull, throbbing or throbbing pain .
The pain increases as it progresses, and the tooth often reacts sensitively to external stimuli such as cold or even a light touch on the spot. The formation of the fistula and the increasing accumulation of pus causes redness or swelling in the form of a bump on the gums . Sometimes the patient’s face also swells on the outside of the affected area.
If a lot of pus collects at the bottom of the fistula,the pus blister bursts and drains the pus into the mouth via the fistula canal. Although this initially provides relief and the pain subsides , the actual cause of the dental fistula is not eliminated. Instead, the inflammation persists, which also progresses the damage to the jawbone . If left untreated, the inflammation can spread and, in the worst case, also attack the bone marrow .
HOW CAN A TOOTH FISTULA BE TREATED?
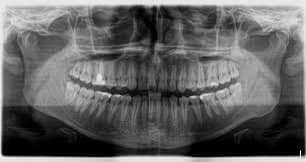
The sooner you see the dentist for a dental fistula, the better . The type of treatment indicated for a fistula on the tooth depends on the cause of the inflammation . In addition to a thorough external examination of the teeth and gums, the fistula can be precisely located using an X-ray finding . It is also possible to see how far the inflammation has progressed.
Antibiotic therapy is usually the most effective
In order to stop the further spread of the bacteria , the dentist usually prescribes an antibiotic. The dosage and duration of intake depends on the severity of the inflammation.
If the fistula is based on an inflamed tooth root , a root tip resection may be necessary. Sometimes the only way to stop inflammation is to remove the affected tooth.
Depending on the size, location, and cause of the dental fistula, minor surgery may be necessary to remove the pus . In order to promote the healing process and minimize the risk of renewed inflammation, antibiotics are also prescribed in this case.
After dental treatment , the healing process should be checked regularly to prevent any complications and renewed inflammation.
Tips for additional support of the healing process
If you notice a tooth fistula in your mouth, you should under no circumstances pierce it yourself or try to express the pus. Improper treatment can make the inflammation worse. The cause of a tooth fistula cannot be eliminated
with home remedies , but the symptoms can at least be alleviated. For example , rinsing with chamomile several times a day or dabbing clove oil on the inflamed area can be helpful to bridge the time until the dentist appointment. However, dental treatment as early as possible cannot replace the use of such home remedies for a tooth fistula. The same is also true for homeopathyfor toothache or inflammatory processes on the gums.
After treatment at the dentist, the use of home remedies – in combination with taking the prescribed antibiotics – can support the healing process if necessary.
IN THIS WAY YOU CAN PREVENT THE DEVELOPMENT OF A DENTAL FISTULA AT AN EARLY STAGE
To prevent fistulas from developing in the mouth in the first place, you should
- Always pay attention to thorough dental care and oral hygiene
- attend regular check-ups at the dentist (every six months)
- Have your teeth professionally cleaned at least once a year in the dental practice
- avoiding potential risk factors for the development of diseases of the teeth and gums, such as smoking, frequent alcohol consumption or a diet high in sugar
In addition, an intact immune system helps to reduce the risk of developing inflammation. A balanced diet rich in vitamins, regular exercise and sufficient sleep have an overall positive effect on health and well-being.